Learning Outcomes
i. Explain Mendel's law of segregation and how it applies to monohybrid crosses.
ii. Describe Mendel's law of independent assortment and its demonstration through dihybrid crosses.
iii. Understand how these Mendelian principles help in predicting the distribution of alleles.
i.Mendel's Law of Segregation
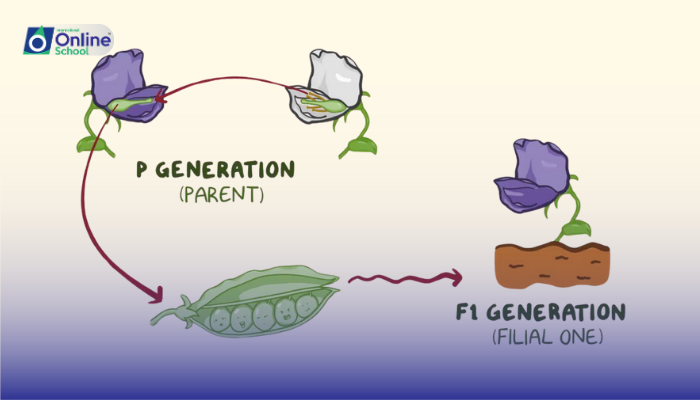
Mendel's law of segregation states that during the formation of gametes (eggs or sperm), the two alleles responsible for a trait separate from each other, or segregate, so that each gamete carries only one allele for each trait. This law is best demonstrated through monohybrid crosses, which involve a single trait.
For instance, if we consider a monohybrid cross between two heterozygous pea plants (Aa x Aa), where 'A' is the allele for purple flowers and 'a' is the allele for white flowers, the law of segregation predicts that each parent will pass on either the 'A' or the 'a' allele to their offspring with equal probability. This results in a genotypic ratio of 1 AA : 2 Aa : 1 aa and a phenotypic ratio of 3 purple : 1 white in the F2 generation.
ii. Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment
The law of independent assortment states that alleles for different traits are distributed to sex cells (& gametes) independently of one another. This principle can be demonstrated through dihybrid crosses, which consider two different traits at the same time.
A classic example of a dihybrid cross is between two pea plants that are heterozygous for two traits (YyRr x YyRr), where 'Y' is the dominant allele for yellow seeds, 'y' for green seeds, 'R' for round seeds, and 'r' for wrinkled seeds. According to the law of independent assortment, the allele a parent passes for one trait does not affect the allele passed for another trait. The F2 generation from this cross would show a phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1 (9 yellow round: 3 green round: 3 yellow wrinkled: 1 green wrinkled).
iii. Predicting Allele Distribution
These laws allow us to predict the distribution of alleles in the offspring. With the law of segregation, we can predict the types of gametes that will form during meiosis. With the law of independent assortment, we can predict the variety of gamete combinations that will occur when more than one trait is considered. Understanding these Mendelian principles is fundamental in the field of genetics, as they provide the basis for understanding inheritance patterns and are foundational to more complex genetic concepts and applications.